Introduction #
In modern mobile development, a robust CI/CD pipeline is crucial for maintaining code quality and ensuring reliable releases. This post explores the CI/CD workflows for both Android and iOS applications, detailing how automation handles everything from pull request checks to store deployments.
Android Workflows #
Our Android CI/CD pipeline is designed to handle multiple scenarios, from verifying code changes in Pull Requests to nightly stability checks and production releases.
We have 3 main builds for android:
- Android Nightly Builds: Runs every midnight
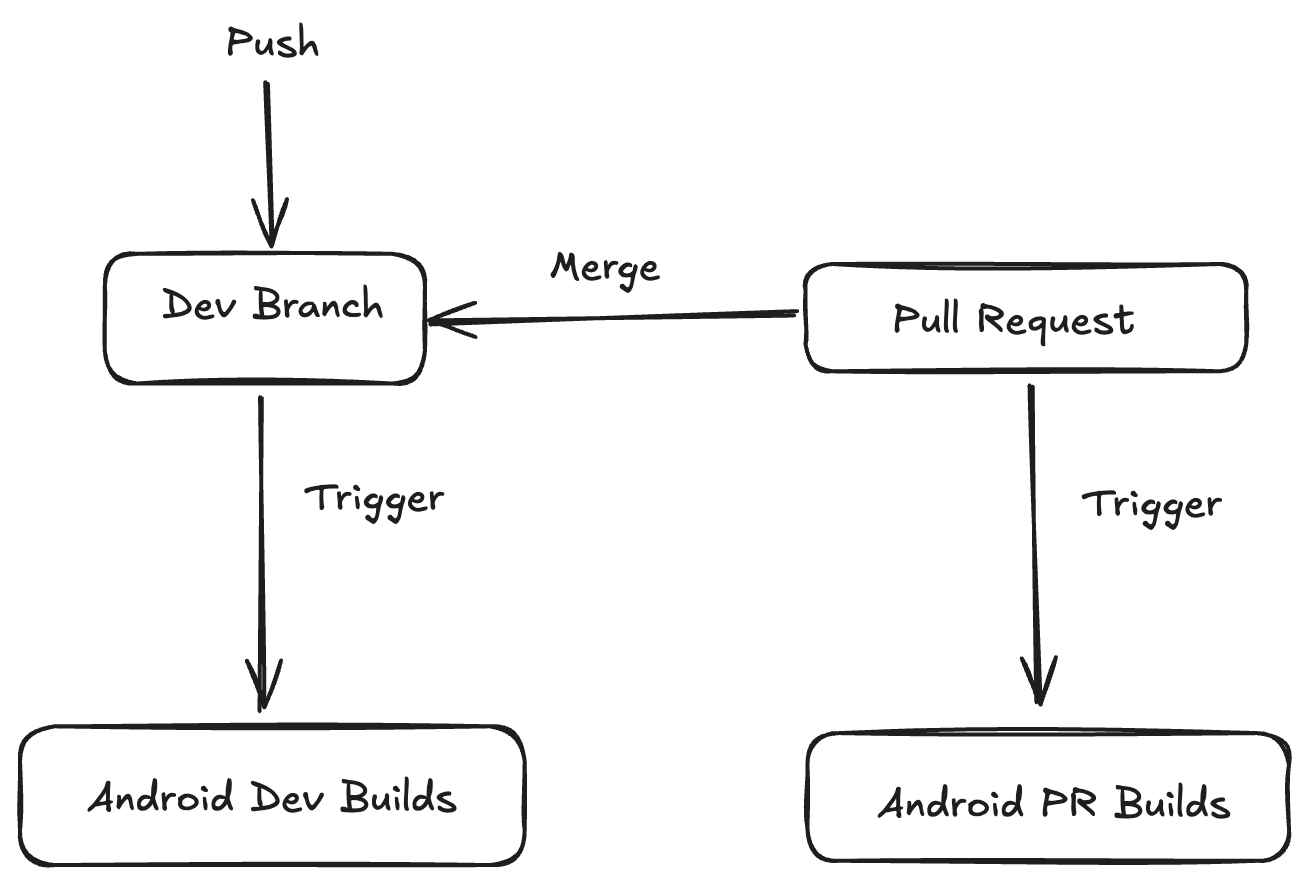
- Android Dev Builds: Runs on push/merge to dev
- Android PR Builds: Runs on PRs with the code from the PR source branch
Self Hosted Github Actions Runner setup #
A single machine can have multiple runners setup to run concurrent jobs. In our case we use mac-minis for our runners.
For android there are 3 runners:
- mac-mini-dev-builds
- mac-mini
- mac-mini-high-priority
1. PR Build Workflow (android-pr-builds.yaml)
#
This workflow ensures that every Pull Request meets quality standards before merging.
- Trigger: Activated on
pull_request_targetevents (opened, synchronized, reopened, labeled/unlabeled). - Pre-checks:
- Validates PR titles and labels (e.g., skips if labeled
WORK_IN_PROGRESS). - Determines build parameters based on labels (e.g.,
PROD_DEPLOYsetsprod_debugbuild type). - Sets build priority: “High” for auto-merge eligible PRs with approvals, “Medium” for others.
- Validates PR titles and labels (e.g., skips if labeled
- Build Process:
- Sets up the environment with specific Gradle memory settings.
- Builds the APK using a custom action (
build-android-apk). - Uploads the resulting APK to S3 for easy testing.
- Quality Gates:
- APK Size Comparison: Compares the new APK size against the base to track bloat.
- iOS Shared Tests: Runs shared tests to ensure Android changes don’t break cross-platform logic.
- Reporting: posts detailed comments on the PR with build status, APK download links, and diff reports. Slack notifications keep the team updated.
2. Dev Build (android-dev-build.yaml)
#
Triggered by pushes to the dev branch, this workflow handles continuous integration and auto-merging.
- Trigger: Push to
devor manual dispatch. - Auto-merge: Checks for PRs labeled for auto-merge and attempts to merge
devback into them if they meet criteria (approvals, mergeable). - Build Process:
- Builds two flavors of the APK: with Dynamic Feature Modules (DFM) and without.
- Uploads both versions to S3.
- Feedback: Sends Slack notifications with download links for both DFM and No-DFM APKs.
Workflow Visualization #
The following diagram illustrates the flow for both PR and Dev builds in our Android pipeline:
graph TD
subgraph PR_Build ["PR Build Workflow"]
A[PR Created/Updated] --> B{Pre-checks}
B -->|Pass| C[Determine Priority/Runner]
B -->|Fail| Z[Skip Build]
C --> D[Build APK]
D --> E[Upload to S3]
E --> F[Compare APK Size]
F --> G[Run iOS Shared Tests]
G --> H[Post PR Comment]
H --> I[Slack Notification]
end
subgraph Dev_Build ["Dev Build Workflow"]
J[Push to dev] --> K[Auto-merge Checks]
K --> L[Merge dev to eligible PRs]
L --> M[Build Dev APKs]
M --> N[Build DFM APK]
M --> O[Build No-DFM APK]
N --> P[Upload DFM to S3]
O --> Q[Upload No-DFM to S3]
P --> R[Slack Notification]
Q --> R
end
classDef green fill:#e1f5fe,stroke:#01579b,stroke-width:2px;
classDef blue fill:#e8f5e9,stroke:#2e7d32,stroke-width:2px;
class A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I green;
class J,K,L,M,N,O,P,Q,R blue;
3. Nightly Build (android-nightly-build.yaml)
#
A scheduled workflow that runs comprehensive tests and builds every night to catch regressions early.
- Trigger: Scheduled cron job at 18:29 UTC daily.
- Parallel Tasks: Runs 10 distinct Gradle tasks in parallel or sequence to verify different configurations (e.g.,
assembleProdDebug,assembleProdRelease, and various flag combinations). - Firebase Test Lab:
- Selects a random mix of 5 physical and 10 virtual devices.
- Runs Robo tests on the
prod_debugAPK. - Reports passed/failed device counts and links to detailed Firebase logs in Slack.
- App Size Analysis: Uses the Spotify Ruler plugin to analyze the app bundle and generate detailed reports on component sizes, uploaded to S3.
3. Play Store Upload (android-playstore-upload.yaml)
#
This manual workflow handles the deployment of the app to the Google Play Store.
- Trigger: Manual
workflow_dispatchwith inputs for version name, version code, and branch. - Release Types:
- Standard Build: Builds a production bundle (
bundleProdRelease) and uploads to S3. - Tagged Release: If a tag is provided, it builds multiple variants (staging, prodReplica, prod) and creates a GitHub Release.
- Standard Build: Builds a production bundle (
- Notifications: Sends Slack notifications with App URLs and build details upon success or failure.
iOS Workflows #
The iOS pipeline focuses on verifying PRs and distributing builds via Firebase App Distribution.
1. iOS PR Build (ios-pr-build.yaml)
#
Similar to Android, this workflow validates changes in iOS Pull Requests.
- Trigger:
pull_requestevents. - Environment Setup: Uses
setup-ios-environmentto configure certificates and provisioning profiles securely using base64 encoded secrets. - Dependency Management: Builds the Android Framework (likely KMP or shared logic) before the iOS build.
- Build: Uses Fastlane (
build_for_develop) to compile the iOS app. - Feedback:
- On failure, uploads build artifacts (logs) to S3.
- Posts a comment on the PR and sends a Slack notification with details about the failure, including log links.
2. Firebase Distribution (ios-firebase-deploy.yaml)
#
Distributes ad-hoc builds to testers via Firebase.
- Trigger: Manual
workflow_dispatchwith inputs for flavour (prod, staging, prodReplica) and release notes. - Process:
- Builds the Android framework dependencies.
- Uses Fastlane to build the IPA and then
distribute_to_firebaseto upload it.
- Output: Generates a Firebase Console URL for the release.
- Notification: Sends a rich Slack message with the release link, commit hash, and flavor details.
3. iOS Dev Build (ios-dev-build.yaml)
#
A workflow triggered by pushes to specific development branches (e.g., develop/2.69.0) to ensure continuous integration during active development cycles.
- Trigger: Push or PR to specific release branches.
- Build: Compiles the app using Fastlane, similar to the PR build, ensuring the dev branch is always in a buildable state.
Conclusion #
These workflows demonstrate a mature CI/CD setup that balances speed (parallel checks, caching) with reliability (comprehensive testing, stability checks). By automating these processes, the team can focus on feature development while confidence in the release pipeline remains high.

